Impeders dramatically improve the efficiency of the welding process by directing more energy towards the
edges of the strip. The high frequency magnetic field created by the work coil induces a current which flows
around the outer surface of the tube. Since the tube is still open at this point, the current then transfers onto
the edges of the strip and flows along them to the point where they are forced together by the weld rolls. The
behavior of electrical currents at high frequencies causes most of the current to be confined to a very thin
layer right at the surface of the strip edge, so rapid heating takes place owing to the resistance of the metal.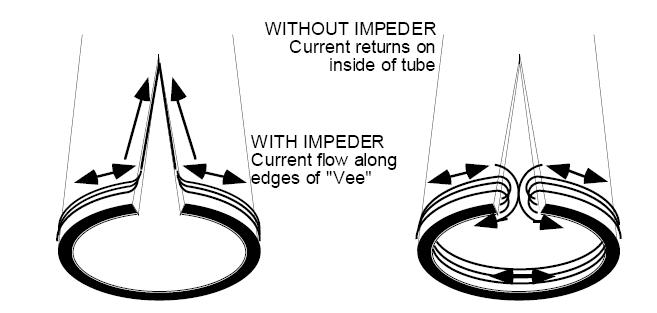
At 450 kHz., the typical operating frequency for induction welding, 90% of the current travels within a few
thousandths of an inch of the material surface, so the current “sees” the inner & outer surfaces of the strip (or
O.D. & I.D. of the tube) as separate conductive paths which are effectively isolated from each other. Without
an impeder. the current which is induced onto the outside surface of the tube can complete the circuit by
returning on the inside surface. This causes the entire tube to heat up, rather than just the edges, and the
energy wasted in doing so may divert enough power away from the edges of the strip to make welding
impossible.
Little can be done to increase the resistance of the inside surface of the strip, but fortunately we are dealing
with high frequencies where resistance is not the only way of opposing current flow. Any electrical circuit
has inductive reactance, which like resistance, is measured in Ohms, and which opposes current flow in a
similar manner. Inductive reactance is zero for direct current, but increases linearly with frequency, and can
be further increased by the introduction of a magnetic core. Ferrite is normally used for this purpose
because it is a poor conductor of electricity and does not therefore heat up to the extent that an iron or other
metallic core would. An impeder is simply one or more ferrite cores contained within a suitable non-metallic
housing.
Baoding Chaochang Electromechanical Co., Ltd.
Copyright © Baoding Chaochang Electromechanical Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved | Sitemap
